Nanotechnology and nanomaterials in the strategy for the treatment of neoplastic diseases
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
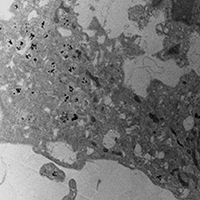
Nanoparticles (NPs) have nanometric dimensions, a large surface-volume ratio, physical and chemical stability and individual optical electronic properties. These characteristics have allowed the use of nanostructured materials for the prevention and treatment of various diseases, such as cancer. NPs have been designed and modified to improve the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs, and to target drugs to cancer cells only. Various nanomaterials can be used for nanomedical applications. In particular, inorganic NPs, such as zinc oxide (ZnO-NPs), gold (Au-NPs) and silver (Ag-NPs) NPs, have been used to improve anticancer therapies. Biosynthesized inorganic NPs were loaded with chemotherapeutic drugs and subsequently functionalized to selectively target cancer cells. Many studies have identified the cellular mechanisms involved after cell-NP interaction: oxidative stress, mitochondrial alterations, lysosomal dysfunction, apoptosis or alternatively autophagy. To improve knowledge of the interaction between drugs loaded on NPs and cells and optimize their use by reducing toxic effects, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques proved to be a good investigation tool. TEM observations have shown, for example, that ZnO-NPs enter the cells by passive diffusion or endocytosis. Ultrastructural analysis showed that Au-NPs enter the cells by invagination of the plasma membrane and are subsequently internalized in the autophagosome. This brief review shows that each new NP needs to be evaluated individually considering all its properties.


 https://doi.org/10.4081/microscopie.2020.9196
https://doi.org/10.4081/microscopie.2020.9196