Effects of IgG from the serum of ischemic stroke patients on hemostasis
Accepted: April 30, 2021
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
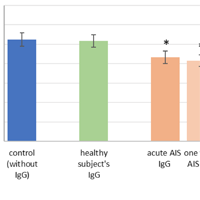
Ischemic stroke is among the top diseases leading to mortality and disability in the world. The detailed investigation of the mechanisms underlying this pathology and especially mediating the tendency to relapse during the first year after stroke incident undoubtedly belongs to important tasks of modern medicine and biology. The current study aims to analyze the influence of IgG derived from the blood serum of ischemic stroke patients on some hemostasis factors. In total, 123 participants with IS, 62 with atherothrombotic ischemic stroke, 61 with cardioembolic ischemic stroke, and 57 subjects as control have been examined. The same patients have participated in the research a year after stroke. IgG from serum was isolated by affinity chromatography on protein A Sepharose column. The activity of key hemostasis factors under the influence of IgG was analyzed. Obtained results revealed that IgG of stroke patients but not healthy subjects caused the inhibition of the amidolytic activity of endogenously generated thrombin, protein C, factor Xa, and led to an increase in the degree of ADP-induced platelet aggregation. The reduction of clotting time in the test "Thrombin time" by IgG of patients at the acute phase of disease was also observed; IgG of healthy subjects mediated the opposite effect. In contrast to acute ischemic stroke IgG, IgG of patients one year after both atherothrombotic and cardioembolic ischemic stroke influenced only the activity of endogenously generated thrombin and factor Xa resulting in inhibition of their activities. It was also established that IgG of ischemic stroke patients, as well as healthy subjects, stimulated the secretion of tissue plasminogen activator by endotheliocytes.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2021.9582
https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2021.9582



