Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Curcumin effects in inducing mRNA gene cathelidicin antimicrobial peptide in Balb/c mice infected with Salmonella typhi
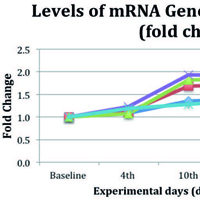
Efforts to combine various herbal compounds are made in the wake of numerous cases of antibiotic resistance. Curcumin is an active compound found in herbal plants. It has an antimicrobial effect that can induce the expression of the mRNA Cathelidicin Antimicrobial Peptide (CAMP) gene and eradicate bacteria. Twenty-five adult BALB/c mice, aged 8–12 weeks and weighing 30–40 grams, were induced with Salmonella typhi at the intraperitoneal cavities. They were randomly allocated in equal blocks to receive CM200 (200 mg/kg of curcumin), CM400 (400 mg/kg of curcumin), CM200+vit D (200 mg/kg of curcumin with vitamin D), and positive control or negative control for 5 days. Mice were then maintained for 3 weeks to count the colonies in the post-intervention period and the level of the mRNA CAMP gene. Real-time PCR was used to measure the expression of the CAMP gene. The level of the mRNA CAMP gene expression significantly increased in CM200 (2.01±0.75) and CM400 (4.06±0.68), pdifference <0.0001. The highest increase of the CAMP gene expression was observed in CM200+vit D (5.47±0.53), pdifference <0.0001. Curcumin increased the expression of the mRNA CAMP gene.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2020.8942
https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2020.8942