Growth, yield, nutrients uptake and anatomical properties of direct seeding and transplanting maize (Zea mays L.) plants under arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and water stress
Accepted: April 26, 2020
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
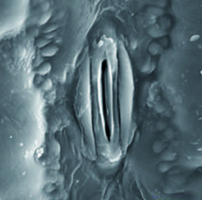
The management of cultivation technology and fertilizer application may adjust adverse effects of abiotic stresses such as water deficit on agricultural products. Therefore, a field experiment was carried out on growth, yield, nutrient uptake and anatomical properties of maize under three water regimes (well-watered, moderate stress and severe stress as 25%, 50% and 75% soil moisture depletion), two cultivations methods (direct seeding and transplanting), and two Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) levels (inoculated with Glomus mosae and uninoculated). The results showed that in plants under moderate water stress, the AMF inoculation percent was significantly higher than those under well-watered and sever stress condition. Inoculation percent in direct seeding was lower than transplanting. Transplanting plants had higher biological and kernel yield compared to direct seeding plants. Water stress reduced the total chlorophyll (Chl) content. Transplanting had greater Chl content in comparison with direct seeding. In all irrigation regimes, transplanting significantly increased N content. In direct seeding, the highest P content was observed in moderate stress and uninoculated plants. Stomatal density increased under water stress, but stomatal size decreased. Plants under severe water stress showed increased stomatal density compared with well waterbed conditions. In addition, severe water stress enhanced the UCT compared to well-watered condition. This study suggests the use of transplanting with AMF application to cope with the adverse effects of severe water stress on maize.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2021.8883
https://doi.org/10.4081/jbr.2021.8883



