Conventional physical therapy combined with extracorporeal shock wave leads to positive effects on spasticity in stroke survivors: a prospective observational study
Accepted: 31 July 2023
HTML: 20
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
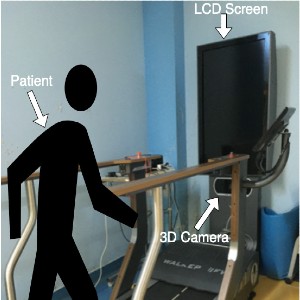
The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (rESWT) and conventional physical therapy (CPT) protocol on the gait pattern in stroke survivors through a new gait analysis technology. Fifteen (n=15) stroke survivors took part in this prospective, observational study and were assessed clinically and through an instrumented treadmill before and after rESWT and CPT. Spasticity grade 95% CI 0.93 (0.79 +/- 1.08), pain intensity 95% CI 1.60 (1.19 +/- 2.01), and clonus score decreased significantly 95% CI 1.13 (0.72 +/- 1.54). The sensorimotor function 95% CI -2.53 (-3.42 +/- 1.65), balance 95% CI -5.67 (-6.64 +/- - 4.69), and gait parameters were enhanced at the end of the program. Step length 95% CI -3.47 (-6.48 +/- 0.46) and step cycle were improved 95% CI -0.09 (-0.17 +/- -0.01), and hip 95% CI -3.90 (-6.92 +/- -0.88), knee 95% CI -2.08 (-3.84 +/- -0.32) and ankle flexion-extension 95% CI -2.08 (-6.64 +/- -4.69) were augmented. Adding the quantitative analysis to the clinical assessment, we gained easy access to track progress and obtained an individualized therapeutic approach for stroke survivors.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.
Similar Articles
- Nicola Manocchio, Isabella Iovene, Antonio Santoro, Maria Chiara Maccarone, Calogero Foti, Report and Abstracts of the 15th Congress of the Mediterranean Forum of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine: Rome, July 6-8, 2023 , European Journal of Translational Myology: Vol. 33 No. 4 (2023)
- Ève Boissonnault, April Jeon, Michael C. Munin, Mirko Filippetti, Alessandro Picelli, Chloe Haldane, Rajiv Reebye, Assessing muscle architecture with ultrasound: implications for spasticity , European Journal of Translational Myology: Vol. 34 No. 2 (2024)
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2023.11607
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2023.11607



