Length-dependent changes of lower limb muscle morphology in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy assessed with magnetic resonance imaging
Accepted: 11 November 2021
HTML: 4
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
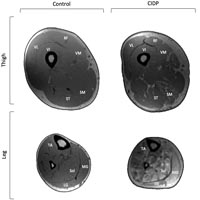
The objective of the present study was to assess muscle quantity of the thigh and leg in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) compared to age and sex matched controls in exploring length-dependent changes of innervated muscles. In five people with CIDP and seven controls, magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess muscle morphology of the four parts of the quadriceps and medial hamstring muscles. Findings were compared to the triceps surae from a subset of participants. The CIDP group had less contractile tissue in the quadriceps (11.5%, P<0.05), hamstrings (15.6%, P<0.05) and triceps surae (35.9%, P<0.05) compared to controls. Additionally, CIDP had less contractile tissue (18.7%) in the triceps surae compared to the hamstrings (P<0.05). Muscle quantity in the quadriceps and hamstrings in CIDP was less than controls, but differences were greater for the distal triceps surae. These findings support a length-dependent affect of CIDP on limb musculature composition.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2021.10200
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2021.10200



