Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Preliminary results of effect of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) extract on liver, pancreas, kidneys and cardiac tissues in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats
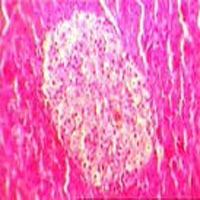
Diabetes mellitus (DM) and its complications impose a significant burden on patients and the health care system. In the Traditional Persian Medicine (TPM), barley is recommended for treatment of DM. This study sought to assess the effect of barley seed aqueous extract on hepatic, pancreatic, renal and cardiac tissues in normal (non-diabetic) and Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Twenty-one male Wistar rats were randomly divided into diabetic and non-diabetic groups. Diabetes was induced by single intraperitoneal injection of Streptozotocin. After one week, the diabetic and non-diabetic groups were randomly divided into control and barley seed extract subgroups namely N group (non-diabetic control rats), S group (seed extract treated non-diabetic rats), D group (diabetic control rats) and DS group (seed extract treated diabetic rats). After 6 weeks, all rats were sacrificed for histopathological analysis and specimens were stained routinely for histological studies. The abnormal histological signs significantly decreased in the DS group compared to D group. Also, protective effects of barley seed extract against histopathological changes were seen in S group compared to N group.These findings suggest that barley seed extract exerts a protective effect on different tissues in diabetes.
Downloads
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10108
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10108