Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Right-sided spontaneous, massive hemothorax in a 27-week pregnant lady: a case report
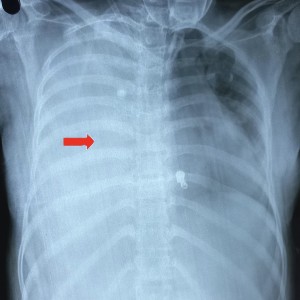
Spontaneous, massive hemothorax due to pulmonary varix is an uncommon, yet catastrophic cause of respiratory distress during pregnancy and postpartum. Presentation is often confused with pulmonary embolism, the treatment of which, worsens the condition. Diagnosis is challenging because of the elusive abnormalities on radiographic and bronchoscopic examination. Currently, there are no treatment guidelines for pulmonary varix. A 23-year-old pregnant lady in her second trimester, with intra-uterine fetal demise, presented to our emergency with dyspnoea, fever, and right-sided chest pain for three days. Chest X-ray and therapeutic thoracocentesis revealed massive right-sided hemothorax and computed tomography suggested pulmonary varix as the cause which was managed with emergency chest tube drainage. Massive, spontaneous hemothorax due to pulmonary varix in pregnancy is a rare occurrence, but it requires timely, multidisciplinary assessment and management for the betterment of the mother and the fetus.
Downloads
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2023.11595
https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2023.11595