Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Ultrasound assessment of diaphragmatic dysfunction and its improvement with levosimendan in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
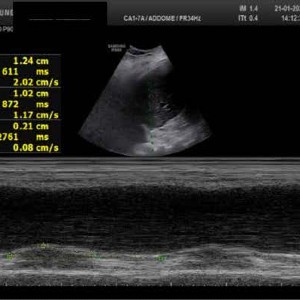
Diaphragmatic Dysfunction (DD) is a clinical condition in which the diaphragm becomes weak or paralyzed, because of muscle strength reduction. It can be due to muscular issues or loss of proper innervation, but, also, to pulmonary hyperinflation or air trapping, such as in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). DD impacts on COPD induced dyspnea, determining its progressive worsening, but levosimendan, an inodilator better known as Ca2+ sensitizer, may limit this phenomenon and diaphragmatic ultrasound assessment can be useful in monitoring its effect. Here, we show the case of a 77-year-old woman admitted to the Emergency department for acute exacerbation of chronic dyspnea in COPD, related to right ventricular failure and DD, which did not respond to medical therapy and non-invasive mechanical ventilation but did experience a favorable outcome after intravenous administration of levosimendan.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2023.11248
https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2023.11248