A case of massive pulmonary embolism causing cardiac arrest managed with successful systemic thrombolytic in the emergency department
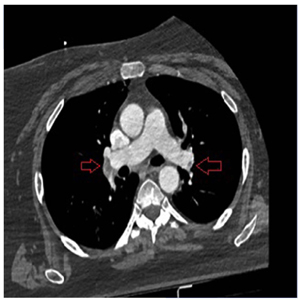
Pulmonary Embolism (PE), when complicated by cardiac arrest, is almost always fatal despite all resuscitative efforts. However, a more favorable is possible when PE is rapidly identified as the cause of cardiac arrest and pulmonary circulation is quickly re-established by specific therapy. A 54-year-old woman was brought to the Emergency Department (ED) by 112 emergency ambulance service with the complaint of shortness of breath that had started 2 hours ago. She developed cardiac arrest while being physical examined 2 minutes after admission, and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) was immediately begun. Massive PE was considered the most likely diagnosis in the light of her history, physical examined, and bedside ultrasonography findings; thus, recombinant tissue Plasminogen Activator (r-tPA) was administered during CPR. The second CPR attempt achieved return of spontaneous circulation within 5 minutes. She was treated at intensive care unit for 32 days and discharged from the hospital with complete recovery.
Downloads
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2022.10827
https://doi.org/10.4081/ecj.2022.10827