Relationship between muscular fitness and bone health in young baseball players
Accepted: 14 February 2021
HTML: 3
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
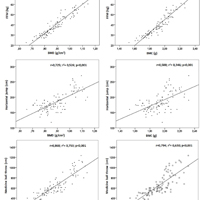
The physical actions developed by baseball players can increase muscular fitness, and consequently improve bone health. The objective was to relate some indicators of muscular fitness to bone health in young baseball players. A descriptive cross-sectional study was carried out in 102 children and adolescent baseball players of the Brazilian National Team. The age range ranged from 9.0 to 15.0 years, the average chronological age was 12.2±2.2 years and the maturity status was 14.8±0.5 APHV (age at peak height velocity). Anthropometry, body composition [% fat, fat mass (FM) and fat-free mass (FFM)], physical tests [horizontal jump (HJ) and medicine ball throw (MBT)] bone health was estimated by anthropometry [bone mineral density (BMD) and bone mineral content (BMC)]. There was positive and significant correlation between bone health with FFM (r2= 89%) and with muscle strength tests (HJ and MBT) (R2= 55 to 75%). Young baseball players classified with low bone health level, reflected decreased values of FFM, HJ and MBT, in relation to young players classified with moderate and high bone health level (p<0.05). It was shown that good bone health is a consequence of a greater presence of muscular fitness, as a result of increased physical activity. These results suggest that emphasis should be placed on those young people who present a greater risk of having low BMD and BMC.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2021.9642
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2021.9642



