Effect of adding dexmedetomidine or remifentanil to thiopental in patients with mood disorder candidate for electroconvulsive therapy
Accepted: 17 March 2020
HTML: 9
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
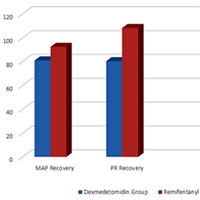
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is one of the appropriate treatments for many neuropsychiatric patients, especially those with mood disorders. Short-term complications of ECT include agitation and postictal. In this study, we compared the addition of dexmedetomidine or remifentanil to thiopental as the main anaesthetic used in ECT. In this double-blind randomised clinical trial, 90 patients with mood disorders (candidates for ECT) were divided into two groups based on their therapy: dexmedetomidine or remifentanil. In the first group (DG), patients were slowly injected intravenously with 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine before induction of anesthesia. In the second group (GR), 100 μg of remifentanil was slowly injected intravenously.In addition, we collected demographic information such as respiratory rate, heart pulse rate, seizure time, mean of arterial blood pressure, recovery duration and the oxygen arterial saturation recorded after recovery. Data obtained were analysed by use of statistical software, SPSS-23. The mean age of both groups was approximately 37 years with the majority being men. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of age and sex, blood pressure, heart rate, duration of seizures and arterial oxygen saturation before ECT. The mean blood pressure and heart rate in the recovery group were lower in the dexmedetomidine group than in the remifentanil group and the hemodynamics in the dexmedetomidine group were more stable. The recovery time in the dexmedetomidine group was longer than that of the remifentanil group (p = 0.001). Both groups had approximately the same satisfaction and the rate of agitation after ECT was the same. Both remifentanil and dexmedetomidine as adjuvants lead to a decrease in patients' post-ECT hyperdynamic responses. In our study, we demonstrated that the effect of dexmedetomidine is greater than remifentanil. On the other hand, neither dexmedetomidine nor remifentanil had a negative effect on seizure duration, but dexmedetomidine significantly prolonged recovery time, when compared to remifentanil.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2020.8877
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2020.8877



