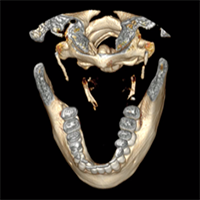
The role of the styloid apophysis of the temporal bone in the biomechanics of the tongue, mandible, hyoid system: a case study
Submitted: 9 January 2020
Accepted: 12 February 2020
Published: 1 April 2020
Accepted: 12 February 2020
Abstract Views: 1291
PDF: 651
HTML: 103
HTML: 103
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Similar Articles
- Giuseppe Messina, The tongue, mandible, hyoid system , European Journal of Translational Myology: Vol. 27 No. 1 (2017)
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2019.8808
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2019.8808




