Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
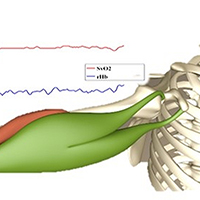
Behavior of oxygen saturation and blood filling in the venous capillary system of the biceps brachii muscle during a fatiguing isometric action
The objective of the study is to develop a better understanding of the capillary circulation in contracting muscles. Ten subjects were measured during a submaximal fatiguing isometric muscle action by use of the O2C spectrophotometer. In all measurements the capillary-venous oxygen saturation of hemoglobin (SvO2) decreases immediately after the start of loading and levels off into a steady state. However, two different patterns (type I and type II) emerged. They differ in the extent of deoxygenation (–10.37 ±2.59 percent points (pp) vs. –33.86 ±17.35 pp, P = .008) and the behavior of the relative hemoglobin amount (rHb). Type I reveals a positive rank correlation of SvO2 and rHb (ρ = 0.735, P <.001), whereas a negative rank correlation (ρ = –0.522, P <.001) occurred in type II, since rHb decreases until a reversal point, then increases averagely 13% above the baseline value and levels off into a steady state. The results reveal that a homeostasis of oxygen delivery and consumption during isometric muscle actions is possible. A rough distinction in two types of regulation is suggested.
Downloads
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2019.8800
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2019.8800