0
0
0
0
 Smart Citations
Smart Citations0
0
0
0
Citing PublicationsSupportingMentioningContrasting
See how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
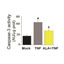
α-linolenic acid reduces TNF-induced apoptosis in C2C12 myoblasts by regulating expression of apoptotic proteins
Downloads
How to Cite
Carotenuto, F., Coletti, D., Di Nardo, P., & Teodori, L. (2016). α-linolenic acid reduces TNF-induced apoptosis in C2C12 myoblasts by regulating expression of apoptotic proteins. European Journal of Translational Myology, 26(4). https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2016.6033
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2016.6033
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2016.6033