Body asymmetries as risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries in dancesport, hip-hop and ballet dancers?
Supplementary Materials: 65
HTML: 56
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
Objectives: The study aimed to determine the incidence and expression of body asymmetries in dancers of three different dance styles: dancesport (n = 14), hip-hop (n = 21) and ballet (n = 20) and to examine how body asymmetries (muscle strength and power, stability and range of motion) are associated with musculoskeletal injuries occurring over the past 12 months.
Design: Cross-sectional and retrospective study.
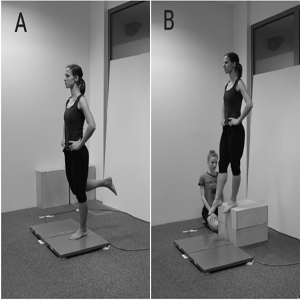
Methods: Maximal isometric voluntary contraction was measured for trunk, hip, knee and ankle movements. Participants performed a single leg stance, unilateral landing, weight bearing symmetry, squat and countermovement jump on force platforms. Passive range of motion was measured for hip, knee and ankle with two-arm goniometer or digital inclinometer (hip flexion, extension and rotations). A retrospective questionnaire was used to collect data on musculoskeletal injuries occurring in the last 12 months.
Results: Different dance styles were associated with different body asymmetries, including strength asymmetries (hip flexion and external rotation), agonist/antagonist asymmetries (trunk flexion/extension, hip abduction/adduction, ankle dorsi/plantar flexion) and hip adduction and internal rotation range of motion asymmetries. Moreover, strength asymmetries of hip flexion, adduction and abduction/adduction as well as stability asymmetries were associated with the total number of musculoskeletal injuries.
Conclusions: The incidence of body asymmetries (> 10%) in dancesport, hip-hop and ballet dancers was confirmed, as well as the association of some asymmetries with self-reported injuries occurring over the last 12 months. The cause-effect relationship should be clarified by further studies.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.11020
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.11020



