Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Cortical bridging a union predictor: A prospective study after intramedullary nailing of the femoral shaft fractures
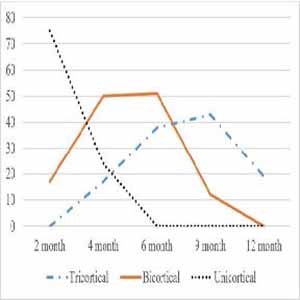
Early prediction of the union helps for timely intervention, reduction of hospitalization, treatment costs, and disability in cases of nonunion. With this in mind, we tried to find how long any cortical bridging predicts the union in femoral shaft fractures. A prospective study of 113 femoral shaft fractures treated with reamed, locked intramedullary nailing was performed. Radiographs were taken during months 2 to 4, 6, 9, and one-year follow-up. The cortical bridging (presence and number) was assessed by anterior-posterior and lateral views. The ROC curve provides the prediction of the union. The overall nonunion rate was 10.6% (12 of 113 fractures). Age and diabetes mellitus were statistically significant with nonunion (p value < 0.001). The final analysis demonstrated that any cortical bridging at four months postoperatively was the most accurate and earlier indicator (105 of 113, 92.9% accuracy), while it was 84.9% at six months in bicortical and 80.5% accuracy at nine months in tricortical bridging. Low-cost and simple radiographic imaging presents cortical bridging in any form 4 months after surgery that precisely predicts a union in femoral shaft fractures.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10835
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10835