Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
The role of bone mineral density and cartilage volume to predict knee cartilage degeneration
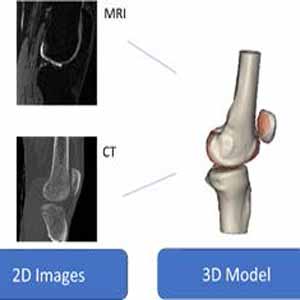
Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) is a highly prevalent condition affecting knee joint that causes loss of physical function and pain. Clinical treatments are mainly focused on pain relief and limitation of disabilities; therefore, it is crucial to find new paradigms assessing cartilage conditions for detecting and monitoring the progression of OA. The goal of this paper is to highlight the predictive power of several features, such as cartilage density, volume and surface. These features were extracted from the 3D reconstruction of knee joint of forty-seven different patients, subdivided into two categories: degenerative and non-degenerative. The most influent parameters for the degeneration of the knee cartilage were determined using two machine learning classification algorithms (logistic regression and support vector machine); later, box plots, which depicted differences between the classes by gender, were presented to analyze several of the key features’ trend. This work is part of a strategy that aims to find a new solution to assess cartilage condition based on new-investigated features.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10678
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10678