The effects of eccentric exercise on passive hamstring muscle stiffness: Comparison of shear-wave elastography and passive knee torque outcomes
Accepted: 23 May 2022
HTML: 45
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
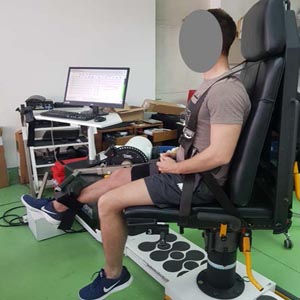
The aim of our study was to assess eccentric-exercise-induced changes in passive knee joint torque, passive knee joint stiffness and shear modulus at of the hamstring muscles. We hypothesized that eccentric exercise would elicit an increase in all outcomes. Fourteen healthy volunteers (age = 25.5±4.7 years) performed eccentric exercise protocol. Before and after 0h, 1h, 24h and 48h, we measured the shear modulus of hamstring muscles using shear-wave elastography and passive knee joint stiffness on isokinetic dynamometer. After eccentric exercise, the shear modulus of biceps femoris increased after 0h (22.4 ± 34.1 %; p = 0.021) and for semitendinosus after 0h (14.5 ± 4.9 %), 1h (16.2 ± 6.5 %) and 24h (16.6 ± 8.3 %) (p = 0.005-0.015). There were no changes for semimembranosus and no changes in passive knee joint moment measures. There were also no correlations between the two methods. Eccentric exercise increased shear modulus of hamstring muscles, while passive joint torque was not affected. This suggests that shear-wave elastography could be more sensitive than torque measures to intra-muscular changes induced by eccentric exercise.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10567
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2022.10567



