A revised model for mitochondrial dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Accepted: 12 September 2021
HTML: 5
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
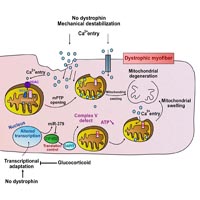
We recently identified a signaling pathway that links the upregulation of miR-379 with a mitochondrial response in dystrophic muscle. In the present commentary, we explain the significance that this pathway may have in mitochondrial dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). We identified the upregulation of miR-379 in the serum and muscles of DMD animal models and patients. We found that miR-379 is one of very few miRNAs whose expression was normalized in DMD patients treated with glucocorticoid. We identified EIF4G2 as a miR-379 target, which may promote mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) in the skeletal muscle. We found enriched EIF4G2 expression in oxidative fibers, and identified the mitochondrial ATP synthase subunit DAPIT as a translational target of EIF4G2. The identified signaling cascade, which comprises miR-379, EIF4G2 and DAPIT, may link the glucocorticoid treatment in DMD to a recovered mitochondrial ATP synthesis rate. We propose an updated model of mitochondrial dysfunction in DMD.
How to Cite
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.

 https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2021.10012
https://doi.org/10.4081/ejtm.2021.10012



